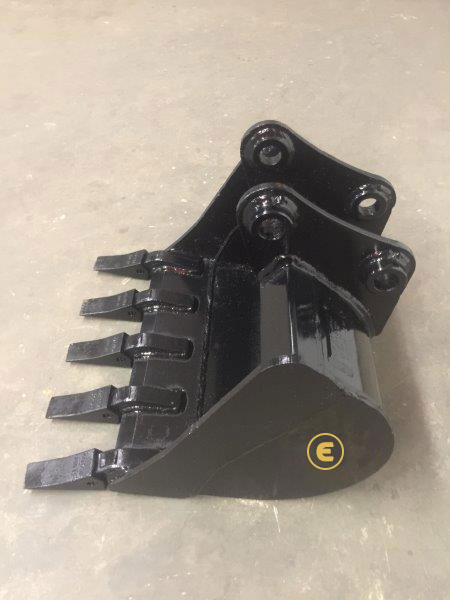
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nulla hendrerit elit eu orci dictum, at aliquam magna egestas. Duis gravida lorem sed turpis dictum interdum. Aliquam semper enim ac ligula iaculis, ut dignissim magna mattis. Mauris et sodales nunc, et blandit eros. Nullam sollicitudin, velit ac gravida finibus, neque dolor suscipit mi, eget vulputate ex felis ut dolor. Sed sit amet commodo purus. Curabitur magna tellus, accumsan id enim nec, fermentum ullamcorper quam. Etiam porttitor ante ut aliquet blandit. Cras dapibus rhoncus cursus. Praesent rhoncus viverra quam, commodo aliquam leo vulputate in. Donec lobortis congue consequat. Sed tempor maximus enim non sodales. Vivamus vel vehicula eros. Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas.
Nunc feugiat purus quis bibendum accumsan. Nam in eros in dolor aliquet vulputate. Proin feugiat enim ac maximus pharetra. Suspendisse eu turpis est. Quisque egestas enim eu nisi hendrerit pretium. Fusce sit amet placerat nibh. Ut feugiat a tellus nec tempus. Cras lobortis ultrices ligula, non malesuada metus facilisis mattis. Fusce at elit tristique, luctus magna non, sodales purus. Quisque nec turpis mi. Phasellus ornare metus dui, eget consectetur erat lacinia id.